The Cybersecurity Challenge Healthcare Organizations are Facing

Hospitals and other healthcare facilities are becoming increasingly reliant on technology for many aspects of their operations. This includes record keeping and patient scheduling. It also extends to medical imaging and surgical procedures. Technology has streamlined many processes. It has improved patient care. Yet, it has also exposed these institutions to cybersecurity threats.

89% of healthcare organizations
reported an average of 43 cyber attacks per year
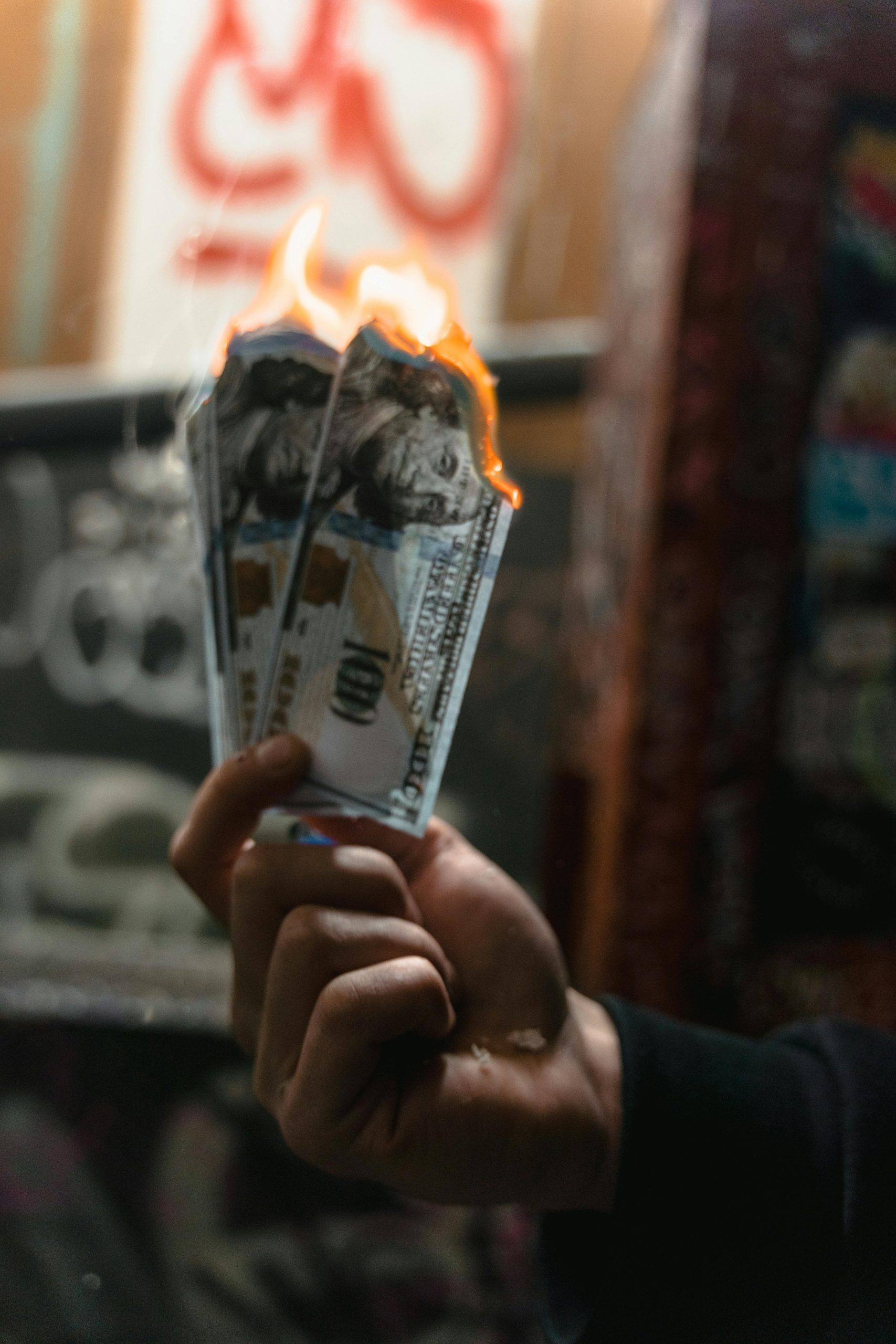

$21,500 per hour to as much
as $45,700 per hour is the average cost of cyber attacks

95% of all identity theft
incidents come from stolen healthcare records
Common cybersecurity threats targeting healthcare organizations
Phishing
Phishing attacks involve fraudulent emails and websites. These trick staff members into disclosing login details or financial information. They also lead to downloading malicious attachments. As a result, there is unauthorized access to sensitive data, financial losses, and a damaged reputation.
Ransomware
Ransomware encrypts vital data. It demands ransom for its release. Malware infiltrates networks and systems. It steals or destroys sensitive information. This results in operational disruptions, loss of data, financial burdens, and legal ramifications.
Data Loss
Data loss can occur due to hardware failure, accidental deletion, or cyber-attacks aimed at destroying or stealing medical information. These incidents can result in disrupted operations, customer dissatisfaction, lost intellectual property, legal liabilities, and even business closure.
User risk
Cybersecurity incidents are often caused by human errors including weak passwords, and clicking on malicious links. Inadequate security practices put sensitive data at risk, leading to financial losses, damaged reputation, and loss of competitive advantage.
Bridging cybersecurity gaps in healthcare
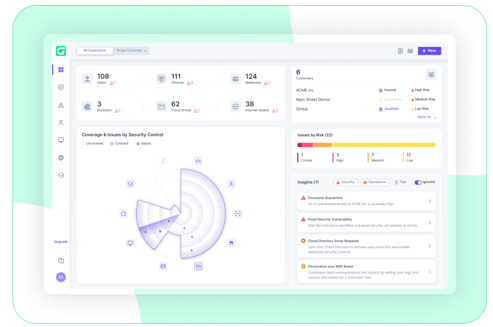
The key to robust cybersecurity in healthcare
Healthcare staff
Healthcare professionals have relatively high turnover rates because of the intense working conditions. They need a comprehensive security solution for both old and new employees.
It s crucial to uphold rigorous cybersecurity practices. This includes real-time protection, regular access reviews, and continual security training. These measures guarantee the safety of sensitive data and system integrity.

Patients
Patients rely on health systems for their well-being. Their personal health information is sensitive. For these reasons, they form an essential demographic in healthcare cybersecurity. A robust security solution should focus on safeguarding patient data in real-time. It should consistently review and control access levels. Maintaining continuous system integrity is also crucial to guarantee dependable patient care and confidentiality.

non-staff care providers
Third-party healthcare personnel introduce unique cybersecurity challenges in healthcare due to their necessary yet conditional access to critical systems. Their security strategy must incorporate real-time safeguards. It should also include meticulous access control and ongoing system protection. These measures manage the distinctive risks they pose while maintaining operational efficiency and data confidentiality.

